Maintaining good oral health through regular brushing and flossing is essential to your teeth and gums. It prevents tooth decay, bad breath, and gum disease. But practicing good oral hygiene is also important in preventing illnesses that affect your overall physical health.
The mouth is highly prone to bacterial growth. Although most of these are harmless, some of them can increase your risk of health problems. As the entry point to your respiratory and digestive tracts, your oral hygiene plays a role in preventing certain bacteria from entering your body.
Oral Diseases that Affect Your Health
Your oral health provides a glimpse into your body. By understanding how oral diseases affect your physical health, you can prevent potential risks. Additionally, you’ll know what to bring up at your next digital orthodontics appointment.
Gum Disease
When plaque builds up along your gums, it creates an environment where different kinds of bacteria thrive. Over time, this can cause an infection. The severity of which depends on how long it remains unchecked and untreated.
- Gingivitis — Considered as the most common type of gum disease, gingivitis cause inflammation of your gums. This causes bad breath and bleeding. When it worsens, it can lead to receding gums and eventual tooth loss.
- Periodontitis — This is a serious gum infection that is often caused by untreated gingivitis. It results in gum inflammation, bad breath, and tooth loss. Additionally, it can cause heavy bleeding in your gums and pus between your teeth.
When either of these gum diseases is left untreated, the bacteria from the infection are absorbed into your bloodstream. It can then attach itself to certain organs, including your heart.
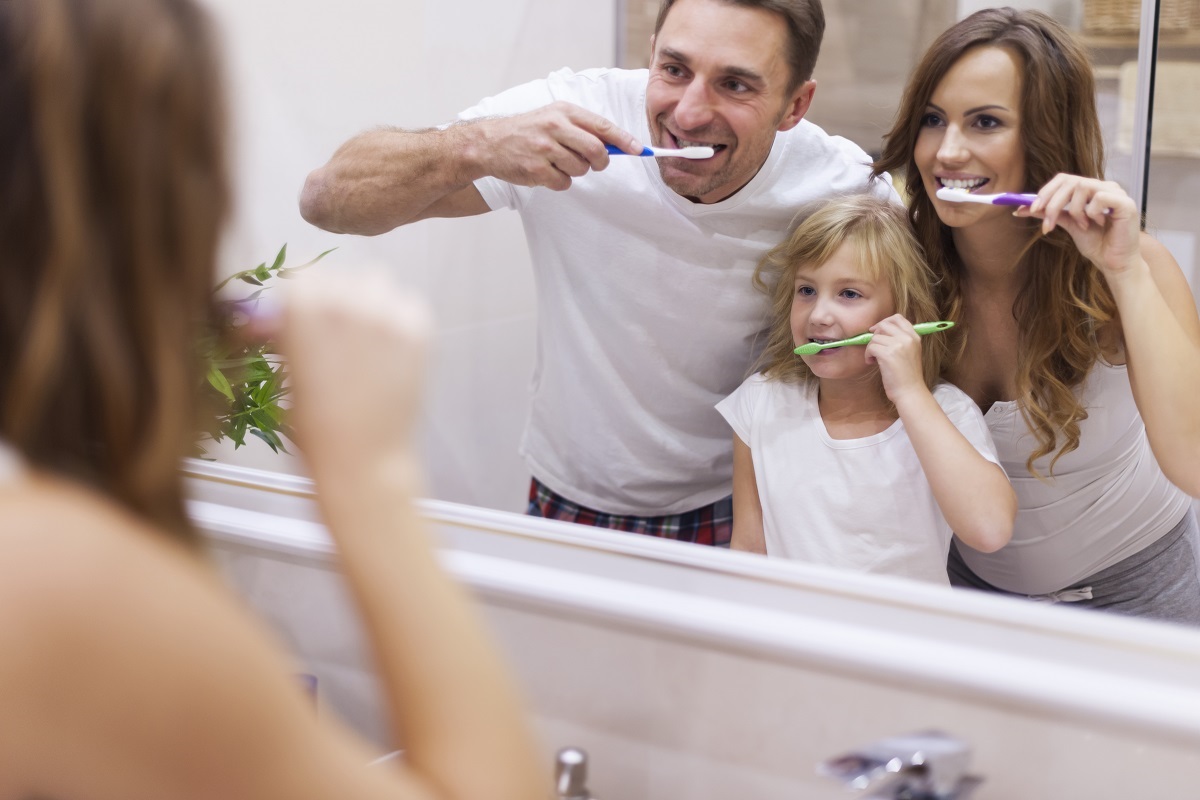

Plaque
Although plaque can evolve into serious gum disease, it can also cause certain health problems by itself. Some studies suggest that the bacteria in plaque can aggravate existing conditions, such as diabetes and HIV/AIDS.
- Diabetes — Severe diabetes increases your risk of developing gum disease. But the latter can also make it more difficult to control your diabetes. Gum infection can disrupt your body’s insulin resistance, resulting in a loss of control over your blood sugar levels.
- HIV/AIDS — With a weakened immune system, you are more prone to different infections, including gum disease. Poor oral hygiene can lead to dry mouth, thrush, and mouth ulcers.
Preventing plaque buildup is necessary to decrease your risk of gum disease. Fortunately, unlike other gum diseases, this is more manageable.
Practices for Better Oral Health
A big part of preventing oral health problems is practicing good hygiene. By making a habit out of healthy practices, you decrease your risk of getting a gum infection and the complications that come with it.
- Practice good oral hygiene. Regularly brush and floss your teeth at least twice a day. If you can, try brushing your teeth after every meal.
- Visit your dentist regularly. Book an appointment with your dentist every six months. These visits can alert you on potential risks before they worsen.
As you learn more about the role your oral health plays in your overall health, you can develop better habits that will prevent illnesses.